VRayShadow
VRayShadow Overview
The VRayShadow plug-in can be used to achieve raytraced shadows with standard 3ds Max lights and V-Ray. Note that in most cases, the standard 3ds Max Ray Traced Shadows will not work with V-Ray. You must use the VRayShadow shadow generator instead. In addition to supporting blurry (or area) shadows, they will also cast correct shadows from objects with V-Ray displacement, as well as from transparent objects.
VRayShadow Parameters
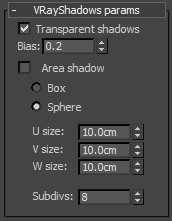 Transparent shadows - this option determines the behavior of the shadows when there are transparent objects in the scene. When this option is on, V-Ray will calculate shadows regardless of the light's Object Shadows settings (Color, Density, Map, etc.), however the color of shadows from transparent objects will be correct. When this option is off, the shadows will take into account the Object Shadows parameters of the light, but shadows from transparent objects will be monochromatic (shades of gray only).
Transparent shadows - this option determines the behavior of the shadows when there are transparent objects in the scene. When this option is on, V-Ray will calculate shadows regardless of the light's Object Shadows settings (Color, Density, Map, etc.), however the color of shadows from transparent objects will be correct. When this option is off, the shadows will take into account the Object Shadows parameters of the light, but shadows from transparent objects will be monochromatic (shades of gray only).
Bias - optionally, V-Ray can compute the shadows at a point that is slightly displaced towards the light from the actual surface being shaded. This may be useful to prevent "surface acne" (black spots on the surface because of incorrect self-shadowing).
Area shadow - turns area shadows on and off.
Type - determines the way in which the area shadows are calculated:
-
Box - V-Ray computes the shadows as if they were cast by a light source with the form of a box.
-
Sphere - V-Ray computes the shadows as if they were cast by a light source with the form of a sphere.
U size - the U size of the light source V-Ray takes into account when computing area shadows (if Sphere light source is selected, U size corresponds to the sphere's radius).
V size - the V size of the light source V-Ray takes into account when computing area shadows (this parameter has no effect when Sphere light source is selected).
W size - the W size of the light source V-Ray takes into account when computing area shadows (this parameter has no effect when Sphere light source is selected).
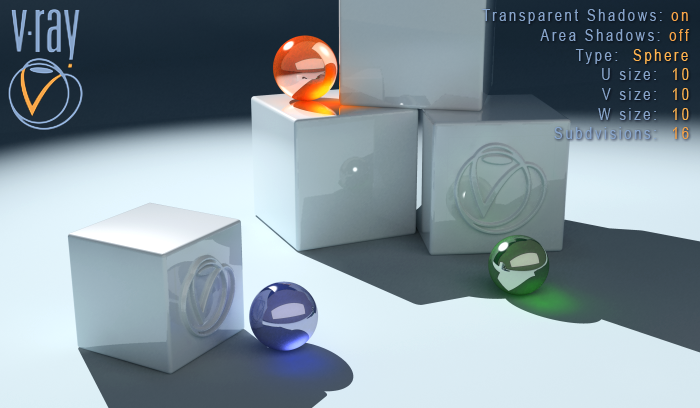
Example: Area Shadow Types: Box vs Sphere / U, V, W Sizes
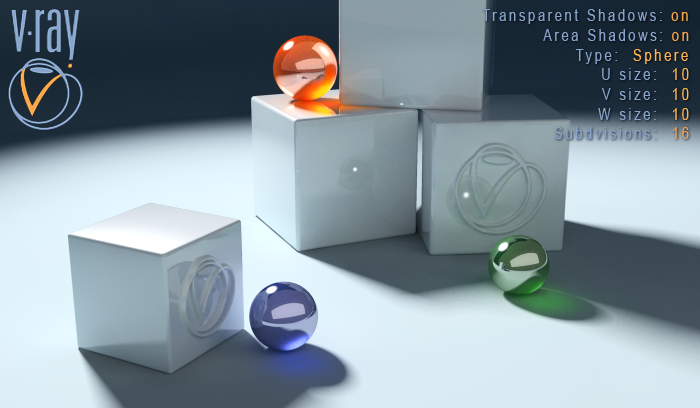

Type Sphere, U: 10, V: 10, W:10
When this type is chosen, the VRayShadow takes under consideration only the U size value. The V and W sizes don't affect the final result. In other words, this means that our light source has a Sphere form and emits rays equally in all directions.
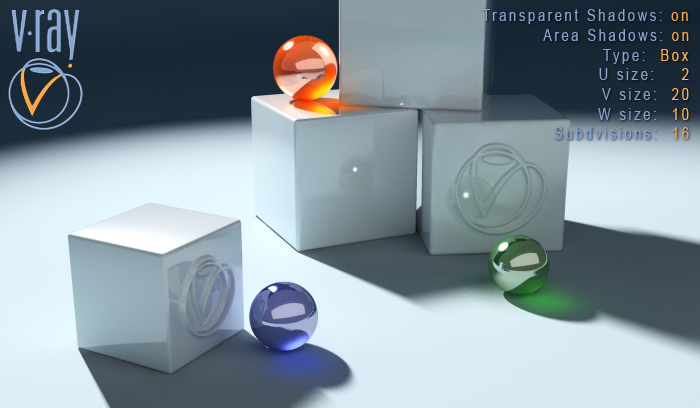
Type Box, U: 2, V: 20, W:10
Now the light source has a Box form. In this case VRayShadow takes under consideration all the U, V, W size values. See how the shadow is strong according to the U axis and is much softer to the V one.
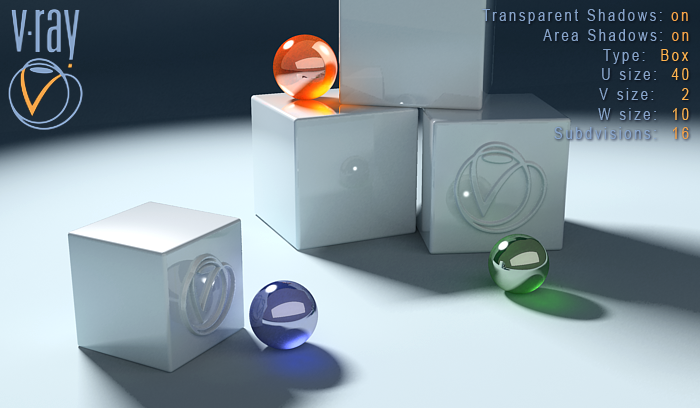
Type Box , U: 40, V: 2, W:10
Now the shadow is looking very different compared to the previous one. You can notice how the size values has influenced the final result of it.
Sub divs - this value controls the number of samples V-Ray will take to compute area shadows at a given point. More subdivs mean less noise, but will render slower.
Example: VRayShadow as Raytraced and Area Types /Subdivisions vs Quality / Bias
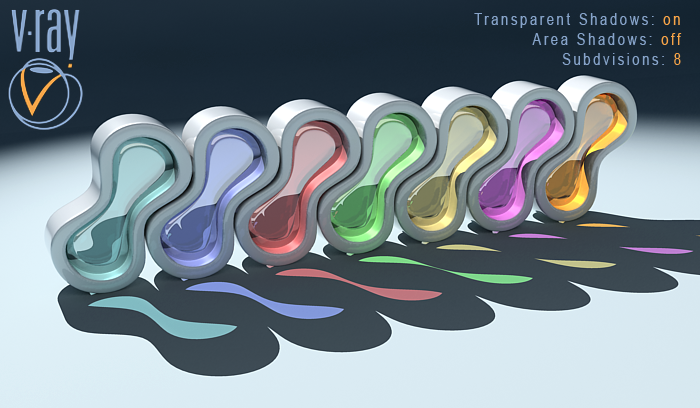
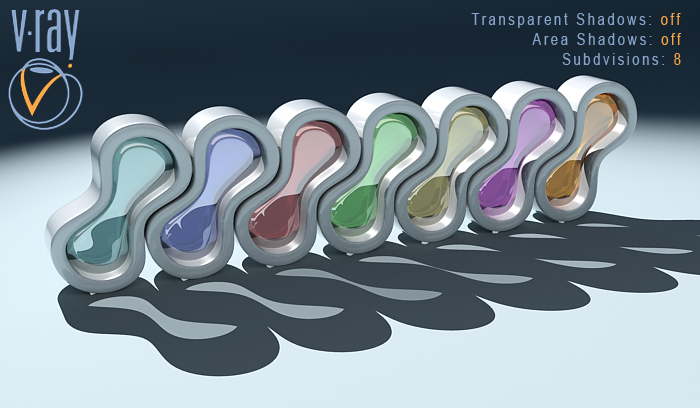
Transparent Shadows: on , Area Shadows: off
Subdivisions: 8
With these settings the VRayShadow acts like a Raytraced Shadow. In this case the Subdivisions have no effect on the final result. Notice that VRayShadow takes in concern only the geometry of the objects and the transparency of their materials (we have colored shadows).
Transparent Shadows: off , Area Shadows: off
Subdivisions: 8
Again VRayShadow acts like a Raytraced Shadow, but this time with Transparency off. Now we still get the transparent level due to the material, but we don't have the colors any more.
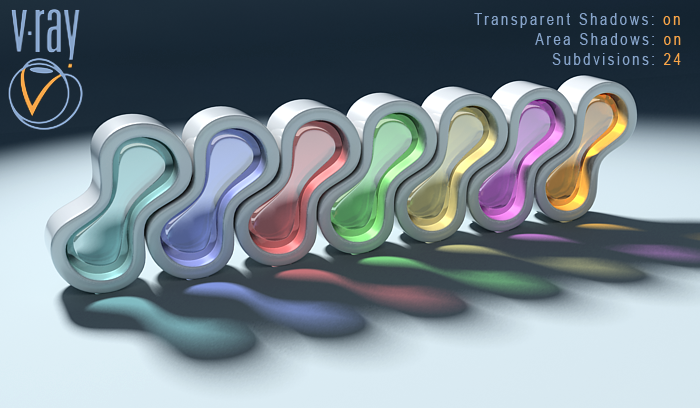
Transparent Shadows: on, Area Shadows: on
Subdivisions: 24
Increasing the Subdivisions leads to better shadow quality. Of course that also leads to higher render time, as V-Ray calculates more samples, You can still notice some grain in the shadow.
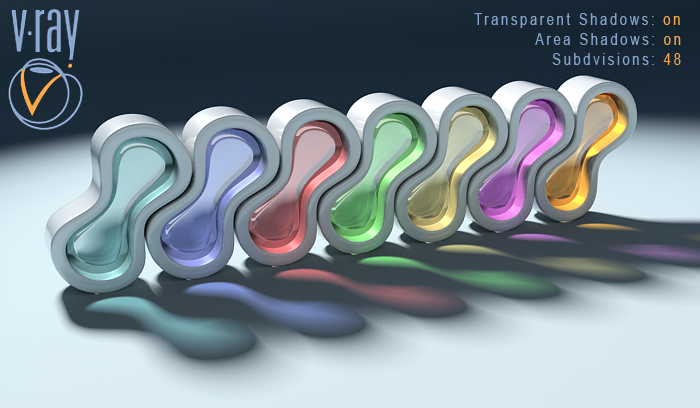
Transparent Shadows: on , Area Shadows: on
Subdivisions: 48
Now with this value of Subdivisions we have a much better shadow quality. Using this parameter wisely can save lots of render time.
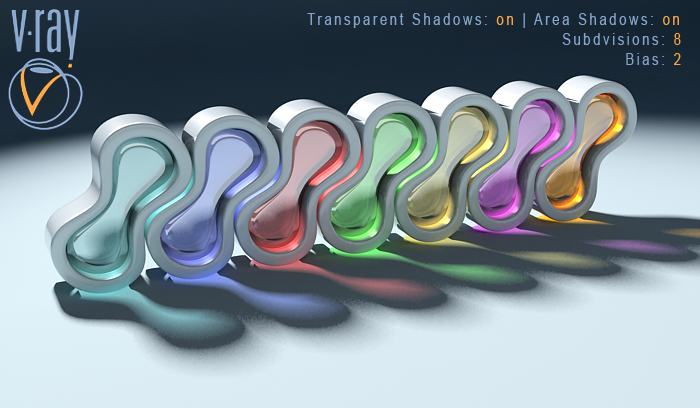

Transparent Shadows: on , Area Shadows: on
Bias: 2.0 , Subdivisions: 8
Biased shadow. Bias moves the shadow toward or away from the shadow-casting object (or objects). If the Bias value is too low, shadows can "leak" through places they shouldn't, produce moire patterns, or make out-of-place dark areas on meshes. If Bias is too high, shadows can "detach" from an object. If the Bias value is too extreme in either direction, shadows might not be rendered at all.
Example: Changing the Shadow Color
Transparent Shadows on.
In this case the Color value (R,G,B) in the Shadow Parameters rollout has no effect. In order to change the shadow color, the Transparent parameter has to be off. See next images.
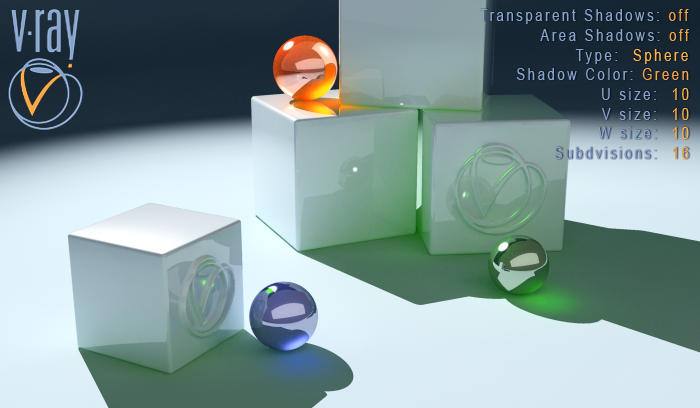
Transparent Shadows off.
Shadow Color Green.
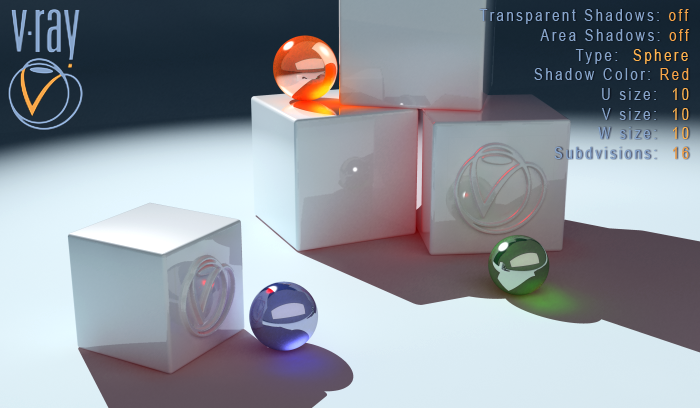
Transparent Shadows off.
Shadow Color Red.