VRayStereoscopic
VRayStereoscopic Overview
The VRayStereoscopic object is a helper that, when added to the scene, allows the user to set up stereoscopic rendering. The helper allows to define two virtual cameras based on the currently selected render camera and the VRayStereoscopic settings, or alternatively the two cameras can be defined explicitly through the VRayStereoRig controller.
VRayStereoscopic Parameters
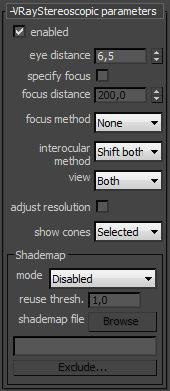 Enabled - enables the VRayStereoscopic helper.
Enabled - enables the VRayStereoscopic helper.
Eye distance - specifies the eye distance for which the stereoscopic image will be rendered.
This parameter is ignored if the current camera has a VRayStereoRig controller (instead the position of the left and right cameras is taken from the VRayStereoRig controller itself).
Focus method - specifies the focus method for the two views. Possible values are:
-
None - both cameras have their focus points directly in front of them
-
Rotation - the stereoscopy is achieved by rotating the left and right views so that their focus points coincide at the distance from the eyes where the lines of sight for each eye converge called fusion distance.
-
Shear - the orientation of both views remain the same but each eyes view is sheared along z so that the two frustums converge at the fusion distance.
This parameter is ignored if the current render camera has a VRayStereoRig contoller.
Interocular method - allows you to specify how the two virtual cameras will be placed in relation to the real camera in the scene.
-
Shift both - both virtual cameras will be shifted in opposite directions at a distance equal to half of the eye distance.
-
Shift left - the virtual cameras are shifted to the left so that the right camera takes the position of the original camera. The left camera is shifted to the left at a distance equal to the eye distance.
-
Shift right - the virtual cameras are shifted to the right so that the left camera takes the position of the original camera. The right camera is shifted to the right at a distance equal to the eye distance.
This parameter is ignored if the current render camera has a VRayStereoRig controller.
View - specifies which of the stereoscopic views will be rendered.
-
Both - both views will be rendered side by side.
-
Left - only the left view will be rendered.
-
Right - only the right view will be rendered.
Adjust resolution - when on this option will automatically adjust the resolution for the final image rendered. For example if you are rendering both views of a 640x480 image it will render one image that has a resolution of 1280x480 with both images side by side.
Show cones - this option controls when to show the cones of the virtual cameras created by the stereo rig. Only the cones of cameras assigned to a view port will be shown.
-
Selected - the cones will be shown only when the stereo rig is selected.
-
Always - the cones will always be shown.
-
Never - the cones will always be hidden.
Shade Map
The shade map parameters allow us to speed-up the rendering of stereoscopic images as well as images with depth of field. The workflow with shade maps involves two stages. At the first stage a shade map is generated by setting the Shademap mode to Render shade map and rendering. We need to specify the file in which the shademap will be saved by clicking on the Browse button before the actual rendering. This will save a file that contains important information about the visible shaded points.We can then use this information later in Use shade map mode to render stereoscopic images or images with DoF much faster.
Shademap mode - allows us to specify the mode of operation for the shade map.
-
Disabled - no shade map will be used during rendering
-
Render shade map - in this mode a shade map will be created and saved in the file specified in the Shademap file field.
-
Use shade map - in this mode V-Ray will render the image using information from the file specified in the Shademap file field.
Reuse threshold - this value affects the rendering with shade maps. Lower values will make V-Ray use less of the shade map and more real shading. This will slow down the whole rendering but may be required if rendering with the default value produces artifacts. When using relatively a relatively large DOF effect, increasing this may help to speed things up.
Shademap file - specifies the name of the file in which the shade map information is stored.
Exclude - allows the user to exclude some of the objects in the scene from being rendered with the shade map. All excluded objects will be rendered without the acceleration from shade maps. This is useful for object like glass windows or large flat mirrors where the stereo effect is needed for reflections/refractions in the material.
Notes
-
The shade map will produce proper stereo effect for opacity-mapped objects, but not for refractive objects. To make it work with refractions, you must exclude the glass objects from the shade map, or use opacity mapping instead.